Why Food Manufacturers Need Product Claim Validation

In today’s competitive and consumer-driven market, product claims are more than just labels, they are promises that build trust, differentiate brands and influence purchasing decisions.
Claims like “high in fibre,” “organic,” “low in sugar,” or “source of vitamins” serve as guiding factors for consumers seeking transparency and value in their food choices. However without proper validation, these claims can backfire, leading to regulatory issues, damage to brand reputation, and legal liabilities. Validating product claims is essential for food manufacturers to ensure accuracy, regulatory compliance and consumer trust.
Here, we explore five compelling reasons why product claim validation should be a top priority for food manufacturers.
1. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
One of the primary reasons to validate product claims is to comply with regulatory standards set by food authorities, such as the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) and similar agencies worldwide. Food regulators are vigilant about the claims companies make on their packaging and in advertisements, as misleading or false claims can harm public health. For instance, if a product claims to be “low in sugar” or “high in protein,” but the actual nutritional profile doesn’t match, it could lead to serious legal repercussions for the manufacturer.
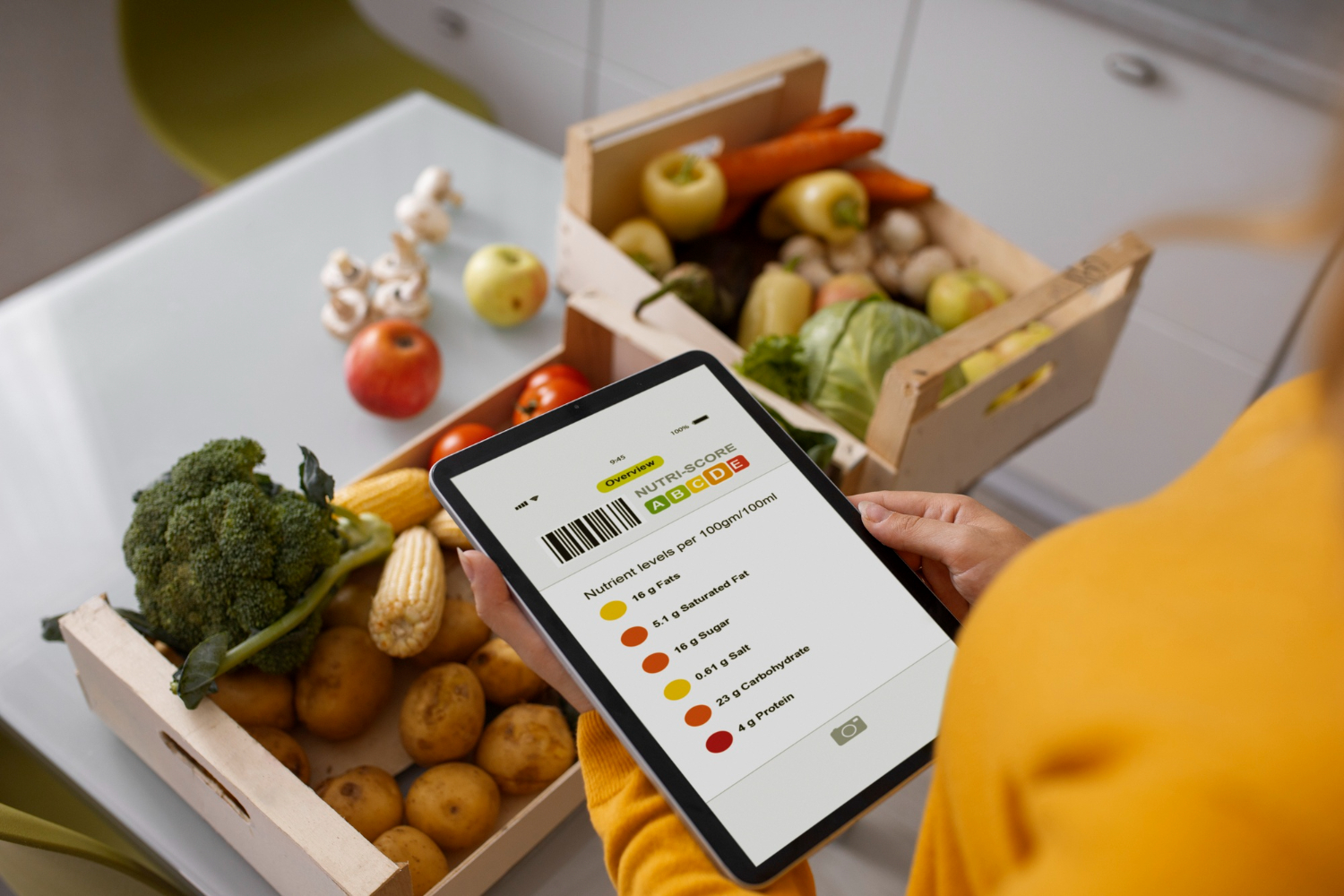
Regulations often require that food manufacturers validate claims through testing or provide scientific evidence supporting these statements. This is where nutritional labelling and food testing become essential. Nutritional labelling must accurately represent the product’s contents, including macronutrients (like fats, proteins and carbohydrates) and micronutrients (like vitamins and minerals). Food testing verifies the accuracy of these labels, ensuring that they comply with regulatory guidelines and genuinely reflect the product’s nutritional value. Failure to meet these standards not only risks fines and product recalls but also damages a brand’s credibility.
2. Building Consumer Trust and Enhancing Brand Integrity
Consumers today are well-informed and increasingly sceptical of product claims. With greater awareness of health and wellness, they seek transparency and honesty in the products they consume. Verified claims contribute to consumer trust and brand integrity, strengthening the bond between manufacturers and their customers.
When a manufacturer accurately validates claims like “organic,” “gluten-free,” or “rich in antioxidants,” it reinforces its commitment to quality and authenticity. However, unverified claims can lead to disappointment or distrust if consumers feel misled. For example, if a product claims to be "100% natural" but includes artificial ingredients, it can lead to public backlash and loss of consumer confidence. By investing in claim validation through rigorous food testing and analysis, manufacturers demonstrate transparency, reinforcing their commitment to truthfulness and integrity in their products.
3. Achieving Competitive Advantage
In a crowded marketplace, product differentiation is key to gaining an edge over competitors. Validated claims serve as Unique Selling Points (USPs) that help food manufacturers stand out from others. Claims like “source of iron,” “no added preservatives,” or “sustainably sourced” appeal to specific consumer segments who value these attributes. When these claims are validated and displayed on packaging, they become powerful marketing tools that attract health-conscious consumers and build brand loyalty.
In addition, validated claims give manufacturers a reputation for quality and reliability, increasing their appeal to retailers, partners, and investors. Food testing to validate claims adds credibility to a brand, enabling it to position itself as a trusted leader in the market. Ultimately, the competitive advantage gained through accurate product claim validation is invaluable, particularly as more consumers prioritise products that align with their values and health goals.
4. Mitigating Legal Risks and Financial Liabilities
Product claims come with accountability. When a food manufacturer makes health-related claims, such as “lowers cholesterol” or “boosts immunity,” there is a legal obligation to ensure the accuracy of those claims. Without proper validation, manufacturers expose themselves to potential lawsuits, regulatory fines, and recalls that can cost millions of dollars.
For example, if a claim about allergen-free ingredients turns out to be incorrect, consumers with allergies may suffer severe reactions, leading to lawsuits and financial liabilities for the manufacturer. Food testing is a crucial step in reducing these risks, as it provides scientific evidence that a product meets the standards stated on its label. Ensuring that each claim is backed by data allows manufacturers to avoid disputes and reduce the likelihood of costly legal battles.
By prioritising product claim validation, food manufacturers take proactive steps to mitigate potential risks and safeguard their business from unforeseen liabilities.
5. Enhancing Product Quality and Safety
The validation process itself contributes to higher product quality and safety standards. Product claim validation often requires in-depth food testing that examines ingredients, nutritional content, and potential contaminants. This rigorous scrutiny not only confirms the accuracy of claims but also helps manufacturers maintain consistent quality across batches, ensuring consumers receive safe, reliable products.
Nutritional labelling and accurate information about ingredients are critical components of product quality. For instance, accurate information on sodium levels or sugar content can be vital for consumers managing conditions like hypertension or diabetes. Through validation, manufacturers uphold their responsibility to deliver the safe, high-quality products they promise.
Furthermore, claim validation encourages manufacturers to regularly assess their quality standards, leading to ongoing improvements in product safety and quality over time.